Krill oil
Krill oil
Description

Krill oil and its natural source
Krill oil, a valuable nutritional source, is extracted from small crustaceans called krill. Krill is a crucial element in the oceanic food chain and is rich in essential nutrients. The primary source of krill oil is Antarctic krill, thriving in the pristine waters of the Southern Ocean. These crustaceans contain a wealth of nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids such as DHA and EPA, as well as Astaxanthin, a carotenoid.
The major advantage of krill oil lies in the extremely high absorbability of omega fatty acids. Omega fatty acids in krill oil exist in the most suitable form: phospholipids. Additionally, these omega fatty acids do not lose quality and efficacy due to the natural presence of the carotenoid Astaxanthin in krill oil. Moreover, there is no overfishing concern with krill oil. The fishing of krill is sustainable and environmentally responsible, unlike the extraction of fish oil, which is no longer considered ecologically or ethically sound.
Benefits of Krill Oil
This natural source of omega-3 fatty acids, such as DHA and EPA, offers numerous health benefits. Here are some of the key health benefits:
- Eye Health: DHA, present in krill oil, supports the condition of your eyes with a daily intake of 250 mg of DHA.
- Brain Function: A daily intake of 250 mg of DHA is beneficial for brain function, as it is a crucial building block for the brain.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: The presence of EPA and DHA in krill oil helps maintain normal blood pressure with a daily intake of 2 grams. Remember that the additional daily intake of EPA/DHA should not exceed 5 grams.
- Healthy Triglyceride Levels: Kala Health Krill Oil contributes to maintaining healthy triglyceride levels in your blood when taken daily at 2 grams. Remember that the additional daily intake of EPA/DHA should not exceed 5 grams.
Composition
Ingredients
Use & dosage
Recommended use
| For Who? | Daily Dosage |
|---|---|
| Adults: | 1 - 2 softgels per day |
Daily dosage: Adults, take 1 to 2 softgels twice daily, or as recommended. Preferably, take during a meal. Adhere to the (recommended) daily dosage.
Mandatory statement: A dietary supplement is not a substitute for a varied diet. A varied, balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle are important. This product is a dietary supplement (fatty acid preparation).
Safety: Consult a professional before using supplements in case of pregnancy, lactation, medication use, and illness.
Storage advice
Background information
What is Krill Oil?
Krill oil, derived from Antarctic krill, are small crustacean creatures thriving in the clean, cold waters around Antarctica. They constitute the world’s largest single marine biomass, with dimensions of up to 6 cm and a weight of about 2 grams. Due to their low position in the food chain, krill oil is virtually free from toxins and heavy metals. Krill, being closer to the source, has a lower risk of accumulating contaminants since they feed on plankton, which forms the foundation of the food chain.
Krill is a rich source of unsaturated fatty acids, particularly the well-known omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA. However, krill also contains other unsaturated fatty acids gaining increasing attention, such as omega-7 fatty acids (palmitoleic acid) and omega-9 fatty acids (oleic acid). In total, krill oil contains omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA bound to phospholipids, astaxanthin, and choline. This combination of essential nutrients, extracted from Antarctic krill, distinguishes krill oil from fish oil and forms the basis for its unique properties.
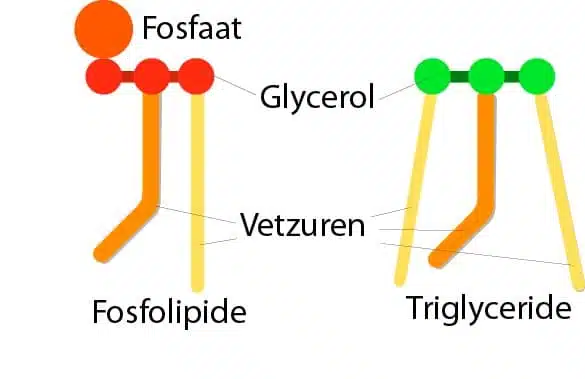
The fatty acids in krill oil are bound as so-called ‘phospholipids,’ a crucial distinction from fish oil. Phospholipids are the building blocks of our body’s cell walls. The phospholipids in krill oil have two fatty acids bound to a glycerol backbone, and this form does not need to be broken down first but can be rapidly and efficiently absorbed by the body. In contrast, fatty acids in fish oil are bound as so-called ‘triglycerides,’ which must be fully broken down before they can be absorbed. Triglycerides consist of three fatty acids with a glycerol backbone. These triglycerides with three fatty acids must first be inefficiently converted before our bodies can absorb this fatty acid variant.
Krill oil offers superior benefits as a source of omega-3 fatty acids for various reasons. For instance, krill oil allows for smaller and easier-to-swallow capsules, does not cause unpleasant fishy burps, contains no additives or preservatives, and is more efficiently absorbed by the body. The phospholipid form in krill oil has been scientifically proven to be more effective and efficient in the absorption of omega-3 fatty acids into tissues compared to triglycerides and ethyl esters in fish oil. This means that a smaller amount of krill oil is needed to obtain the same benefits of omega-3 fatty acids compared to fish oil.
Ultimately, key components of krill oil, such as phospholipids, choline, and omega-3 fatty acids, have demonstrable effects in the cells and tissues of the body, forming the basis for health benefits in various body systems and health conditions.
What are the Health Effects of Krill Oil?
Kala Health’s Krill Oil softgels offer numerous health benefits for our body. This powerful formula not only supports the heart but also the liver. We know that regular intake of krill oil can contribute to the normal functioning of the heart, thanks to the presence of EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Furthermore, these softgels contain choline, which is essential for the regulation of homocysteine metabolism and the normal metabolism of lipids in our body. Choline also contributes to maintaining normal liver function. So, if you are looking for a natural way to support your cardiovascular health and normal liver function, krill oil is an excellent choice. Discover the benefits of Kala Health’s Krill Oil softgels and invest in your well-being.
What are the Health Claims of Krill Oil?
In addition to astaxanthin, krill oil contains the following fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, Omega-6 fatty acid LA, Omega-7 fatty acid Palmitoleic acid, and Omega-9 fatty acid Oleic acid.
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid):
*The additional daily intake of EPA and DHA combined should not exceed 5 grams.
- Good for the heart: with a daily intake of 250 mg EPA and DHA. Contributes to maintaining normal blood pressure: with a daily intake of 3 grams of EPA and DHA.
- Contributes to a normal blood fat level: with a daily intake of 2 grams of EPA and DHA.
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid):
*The additional daily intake of EPA and DHA combined should not exceed 5 grams.
- Good for the heart: with a daily intake of 250 mg EPA and DHA.
- Contributes to maintaining normal blood pressure: With a daily intake of 3 grams of EPA and DHA.
- Contributes to a normal blood fat level: with a daily intake of 2 grams of (EPA and) DHA.
- Good for vision: with a daily intake of 250 mg DHA.
- The intake of DHA by the mother supports the normal development of the fetus’s eyes and in infants receiving breast milk: with a daily intake of 200 mg DHA in addition to the recommended daily intake for omega-3 fatty acids for adults, i.e., 250 mg DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA).
- DHA contributes to the optimal visual development of infants up to the age of 12 months: with a daily intake of 100 mg DHA.
- The intake of DHA by the mother is good for the development of the fetus’s and infants’ brains receiving breast milk: with a daily intake of 200 mg DHA in addition to the recommended daily intake for omega-3 fatty acids for adults.
- Good for brain function: with a daily intake of 250 mg DHA.
ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid):
- Good for cholesterol: with a daily intake of 2 grams of ALA.
- Essential fatty acids are good for the normal growth and development of children: with a daily intake of 2 grams of ALA (and a daily intake of 10 grams of LA).
For Whom is Krill Oil a Suitable Product, and is Krill Oil Sustainable?
Krill oil is sustainable and is therefore suitable for those striving for a healthier and more sustainable alternative to fish oil.
Krill oil is clean, sustainable, and traceable. Fish populations are overfished globally, and the origin of fish oil is almost always unknown. With krill oil, we know exactly where it comes from, and there is no risk of overfishing. Krill fishing takes place in the pristine Antarctic waters and is under the full control of the Commission for the Conservation of the Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR), an international agreement regulating the sustainable harvest of krill. In Zone 48 in the Southern Ocean, the only area where krill fishermen are allowed to operate, the krill industry is permitted to catch only one percent of the estimated 60 million tons of krill.
To meet the global demand for omega-3 fatty acids while the pressure on fish stocks increases, new sustainable sources are needed. Krill oil is one such source, and the World Wildlife Fund emphasizes clearly: Krill management is sustainable. Krill fishing is sustainable and ecologically responsible, using a newly developed patented fishing method that yields no unnecessary bycatch.
Additionally, krill oil comes from a sustainable source and has undergone extensive analyses to determine the presence of contaminants such as dioxins, furans, dioxin-like PCBs, organochlorine pesticides, PBDEs, heavy metals, PAHs, arsenic species, fluoride, trans-fatty acids, and marine algae toxins. The clean living environment of krill, combined with its position at the bottom of the food chain, prevents the accumulation of these contaminants often found in marine life higher in the food chain. Moreover, the quality of krill oil has been improved by reducing TMA/TMAO and salt levels, resulting in virtually taste- and odorless krill oil concentrates. The concentrations of phospholipids, choline, and omega-3 fatty acids have been increased, providing a unique combination of these essential nutrients in the krill oil concentrate.
Availability and Absorbability
Various studies indicate that krill oil is better absorbed than fish oil and has significantly higher biological availability. This is important for two reasons:
- It is cost-effective. Less krill oil is needed to obtain sufficient omega-3 fatty acids.
- There is no risk of getting too many omega-3 fatty acids. Numerous studies show that excessive DHA and EPA intake can be harmful to the body, negatively affecting the immune system and blood sugar levels, among other things. The high doses of fish oil recommended sometimes approach a potentially harmful dose. It is better to take a low dose of krill oil.
Why Krill Oil in Softgels?
Kala Health’s Krill Oil softgels are filled with high-quality krill oil. Each softgel contains 500 mg of top-quality krill oil. Our softgels are manufactured using an advanced fusion technique, where the capsule halves are hermetically sealed together, fully protecting the contents from external influences. Compared to common softgel capsules, Kala Health’s krill oil softgels have significantly less odor. Moreover, they retain their quality longer and hardly cause unpleasant burps after ingestion.
Why is Krill Oil Superior to Fish Oil?
Important fatty acids like EPA and DHA are also found in fish oil, but there is a crucial difference: In fish oil, fatty acids are bound as so-called ‘triglycerides.’ Three fatty acids are attached to one molecule of glycerol. In krill oil, however, one of the three fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate group that is hydrophilic (water-loving). Due to the phosphate group, we call the fats in krill oil ‘phospholipids.’
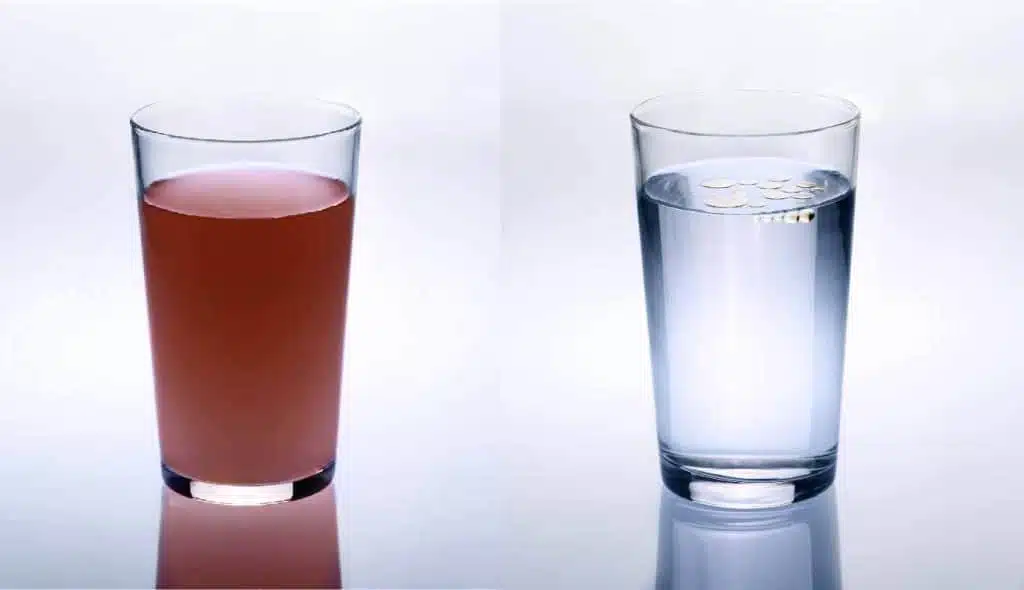
Krill Oil by Kala Health Fish oil remains in large drops floating on water (glass on the right in the photo). If krill oil is placed in a glass of water, the oil forms microscopic small spheres that mix with the water (glass on the left in the photo). The same happens in the stomach. Therefore, krill oil is less likely to cause an aftertaste and burps. These spheres are rapidly and directly absorbed into the blood from the small intestine. Since phospholipids are body-specific, they are also quickly and effectively incorporated into the body.
Krill Oil vs. Fish Oil by Kala Health Triglycerides from fish oil, on the other hand, are not body-specific; to absorb them, they must first be split into glycerol and separate fatty acids. This occurs in the intestine through the action of bile and the enzyme lipase. After absorption, the fatty acids are reattached to a glycerol molecule and built into, for example, triglycerides or phospholipids.
Stability
Phospholipids are more stable than triglycerides. As a result, krill oil remains stable, while fish oil quickly oxidizes in the air. Krill oil has another significant advantage: it naturally contains astaxanthin, a special carotenoid produced by certain microalgae and plankton. It is interesting to note that astaxanthin is the pigment that gives salmon their pink-red color. Astaxanthin has accumulated in the muscle tissue of salmon for a reason: it helps pair-ripe salmon undertake their energy-consuming migrations to upstream spawning grounds in the river every year.











 60 or 180 softgels
60 or 180 softgels
 250, 500, 1.000 or 5.000 gram
250, 500, 1.000 or 5.000 gram
 50 gram
50 gram
 60 or 180 capsules
60 or 180 capsules