Astaxanthin
-
- 100% Plant-based: Contains astaxanthin-rich oleoresin, extracted from the algae Haematococcus pluvialis
- Protection of healthy body cells: Vitamin E contributes to the protection of cells against oxidative damage
- Top quality ingredients: produced in the EU
Description

What is Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin is a red pigment produced by the tiny algae Haematococcus pluvialis. Scientists believe that thanks to the protective effect of astaxanthin, this algae can survive for decades without food and water. When the algae is exposed to harmful UV light (sunlight), it produces astaxanthin as a natural protection to survive.
Through the food chain, astaxanthin accumulates in, for example, fish (such as salmon) and lobster, giving their flesh a pink color. These are natural sources of astaxanthin. Scientists believe that the high concentration of astaxanthin in muscle tissue plays an important role for salmon. It enables mature spawning animals to undertake the annual migration to the upstream spawning grounds, overcoming incredible obstacles. Imagine, an adult human having to swim against a strong current for weeks on end without interruption, overcoming towering waves and sometimes dozens of meters high waterfalls? A human could never endure this and their muscles would acidify completely due to oxidative stress in a short time. But a salmon can achieve such performances, partly due to the high concentrations of astaxanthin in the muscles.
Those who want to take astaxanthin can do so by regularly eating wild salmon. Note: almost all Norwegian (or Atlantic) salmon is artificially farmed salmon to which synthetically made astaxanthin is added to the feed to color the flesh pink. Farmed salmon is therefore not a good source of natural astaxanthin!
Natural source of Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin occurs naturally in plants and certain microorganisms such as plankton, algae, fungi, and bacteria. It is mainly produced by microalgae, such as Haematococcus pluvialis, which thrive in freshwater environments. These microalgae are able to synthesize large amounts of astaxanthin, making them an essential source.
The pink pigment we know from various aquatic animals such as shrimp, trout, crab, and some birds like the flamingo, is due to astaxanthin. It enters the food chain via algae and plankton.
The quality of Astaxanthin
The astaxanthin used in Kala Health’s Astaxanthin formula is from a renowned brand, known as NatAxin®, and is produced by a Chilean biotechnology company.
The astaxanthin is produced in the Atacama Desert, which is globally known for its pristine nature. Furthermore, the location of the desert is far away from agricultural or populated areas, making cultivation safe and free from environmental pollution. The algae are cultivated in (purified) spring water from the surrounding Andes Mountains, and bathed in vast amounts of sunlight.
After harvest, the algae are carefully vacuum-dried at low temperature and ground. From this powder, the so-called ‘astaxanthin-rich oleoresin’ is extracted. The astaxanthin-rich oleoresin is used in Kala Health’s Astaxanthin formula.
The careful production process ensures that the nutrients are characterized by very high biological availability and are completely free from unnecessary solvents.
The text continues below the image.
Atacama Desert

Astaxanthin, Eyes, and Brain
Astaxanthin is one of the few substances capable of crossing both the blood-brain barrier and the blood-retinal barrier. As a result, astaxanthin absorbed through diet also reaches these organs and exerts its effects there.
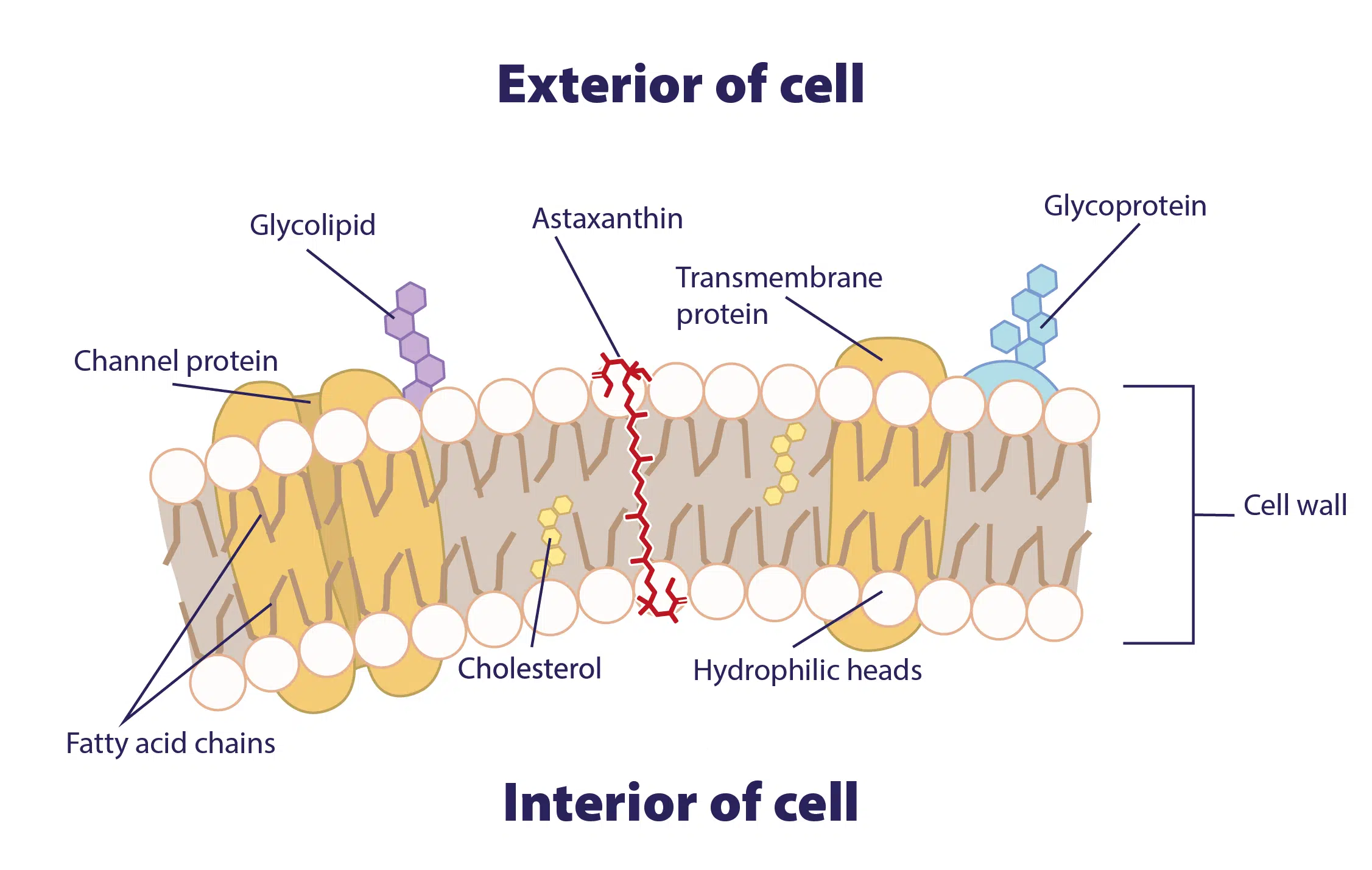
ASTAXANTHIN SPANS BOTH INSIDE AND OUTSIDE OF CELL MEMBRANE
The illustration below shows that astaxanthin can attach to the cell membrane and span both the inside and the outside. Similar natural ingredients such as vitamin C and beta-carotene, for example, cannot do this.
Functioning of Astaxanthin in the Cell Membrane
ASTAXANTHIN NEVER BECOMES A PRO-OXIDANT
Under certain conditions, antioxidants themselves can become so-called ‘pro-oxidants’ (free radicals) and undermine health. Well-known examples are ß-carotene, lycopene, and zeaxanthin, but also vitamins C and E. However, natural astaxanthin is an exception to this: it will never become a pro-oxidant.
- Contains natural astaxanthin, and vitamin E
- Top-quality ingredients, produced in the EU
- Contains astaxanthin-rich oleoresin, extracted from the algae Haematococcus pluvialis, while preserving all valuable substances
Authorized health claims:
Vitamin E:
– Vitamin E contributes to the protection of cells from oxidative damage
Emphasis on Note
Due to legal restrictions, not all details about this dietary supplement can be provided. However, for further inquiries, we can be reached at +31 (0)70-345-0290.
Composition
Astaxanthin from Kala Health contains the following ingredients:
Ingredients
| Each capsule contains: | %RDA | |
|---|---|---|
| Astaxanthin (Nataxin™) | 4 mg | - |
| Palm-free MCT oil | 210 mg | - |
| DL-alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) | 1.8 mg | 15% |
Ingredients: Bulking agent (MCT oil), modified pea starch, Astaxanthin-rich oleoresin from algae (Haematococcus pluvialis), carrageenan, glycerol, vitamin E.
Guaranteed free from: yeast, sugar, lactose, gluten, soy, GMO, preservatives, synthetic fragrances, colors, and flavors. Suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
Use & dosage
Recommended use
| For Who? | Daily Dosage |
|---|---|
| Adults: | 1 to 2 capsules per day |
| Children: | Adjust the dosage based on body weight |
Daily dosage: adults 1 to 2 capsules per day, or as recommended. Not suitable for children under 14 years of age. Do not use if consuming other supplements with astaxanthin esters on the same day. Adhere to the recommended dosage. Preferably take during a meal. Adhere to the (recommended) daily dosage.
Mandatory statement: A dietary supplement is not a substitute for a varied diet. A varied, balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle are important. This product is a dietary supplement (contains vitamins). This product is a dietary supplement (contains pea starch, fatty acids, and vitamins).
Safety: Consult an expert before using supplements in case of pregnancy, lactation, medication use, and illness.
Storage advice
Storage: Keep in a dry place at room temperature and out of the reach of small children.









