OptiMSM
OptiMSM® capsules, tablets, powder and gel
OptiMSM®: The purest form of MSM
MSM (methylsulfonylmethane) is a small molecule with significant importance for the body. The chemical formula of MSM is CH3SO2CH3. It is a small, light molecule with a molecular weight of 94, making it very easily absorbable by the body. MSM is the form in which sulfur naturally occurs in all living organisms and is biologically active. MSM is naturally found in fruits, vegetables, and for example, in the milk of grazing cows in pastures. It is an odorless, white powder that dissolves well in warm water and in a wide range of organic solvents.
MSM has been studied for over forty years by scientists affiliated with the Health Sciences University in Oregon, United States, under the leadership of Professor Stanley W. Jacob M.D. Dr. Jacob has documented his experiences in several books: “The Miracle of MSM, the Natural Solution for Pain” (1999) and “MSM, the definite guide” (2003).

OptiMSM® is the purest form of MSM available, manufactured by Bergstrom Nutrition in the United States and uniquely purified through multiple distillation processes. OptiMSM® is also the only MSM with published, peer-reviewed research. OptiMSM® is the only MSM in the world produced according to the global patents of Robert J. Herschler.
The different types of MSM
“There are two qualities of OptiMSM® powder. Firstly, there is the ‘Microprill‘ quality. This is a fine powder in which the crystals easily stick together. This quality is primarily intended for tabletting, requiring very few fillers. To keep the powder manageable, 0.1% silicon dioxide has been added (silicon dioxide is nothing more than finely ground sand!). So, you could say that this quality of OptiMSM® is 99.9% pure.
The second quality of OptiMSM® is the ‘Flake‘ quality. These crystals are coarser and stick together less. ‘Flakes’ are mainly intended for mixing into feed and dissolving in water or fruit juice. However, due to the larger crystals, it takes a little longer to dissolve than with ‘Microprills’. OptiMSM® ‘Flakes’ not only mix more easily into feed, but no silicon dioxide is added. Therefore, you can say that the ‘Flake’ quality is 100% pure.”

Primitive Supplier of Sulfur
The element sulfur belongs to the same main group as the element oxygen. Sulfur and oxygen are therefore closely related. In oxygen-deprived environments, organisms often use sulfur instead of oxygen as a source of energy. In 1986, an underground cave was discovered in Romania that likely had not been in contact with the outside world for five million years. In the cave, a total of 48 new invertebrate species were discovered. These animals owe their existence to warm, upwelling, sulfur-rich water that fills the cave with high concentrations of hydrogen disulfide (H2S). For humans, this sulfur-rich gas would be deadly. For the bacteria, fungi, and animals in the cave, it forms the basis of life.
We must consider that hundreds of millions of years ago, oxygen was scarce on Earth. It wasn’t until land plants began to evolve that the oxygen content in the atmosphere increased. Even then, it took a long time for the oceans to absorb the oxygen. We know that hundreds of millions of years ago, algae in the oceans began to produce simple organic sulfur compounds, such as MSM. These sulfur compounds were likely the first and most important sources of energy for all life forms that subsequently evolved. This supports the idea that higher life forms may be genetically programmed to use MSM as a sulfur source.
In various studies involving laboratory animals, MSM with radioactively labeled sulfur (35S) was administered orally. These studies revealed that MSM is partially broken down after oral intake, and the released sulfur is utilized by the body. The radioactive sulfur (35S) was found in the collagen and keratin of hair and nails. Surprisingly, radioactive sulfur was also detected in the amino acids methionine and cysteine, as well as in the proteins of the blood serum. This discovery demonstrates that sulfur derived from MSM is incorporated into the so-called methionine metabolism.
“Primitive” Supplier of Methyl Groups
Methyl groups are the building blocks of all organic molecules. The body is constantly breaking down tissues and cells and rebuilding them. Millions of times per second, methyl groups are made available to molecules in our bodies. This process, called methylation, affects all life processes. Without methyl groups, new DNA cannot be formed, and therefore, new cells cannot be made. The formation of a large number of molecules also depends on methyl groups, including certain neurotransmitters such as choline, serotonin, norepinephrine, and adrenaline. Methyl groups are also essential for the detoxification processes in the liver. Both the physical and mental health of humans depend on an adequate supply of methyl groups.
The interesting fact now arises that the molecule MSM is composed of two methyl groups and one sulfur atom (as a sulfate group). A molecule of MSM is broken down in the body into a sulfate (sulfur) group and two methyl groups, with no residual substances remaining. It is almost certain that MSM has been an important and perhaps the only supplier of methyl groups for the primitive life forms that developed hundreds of millions of years ago. Are all other life forms that have developed since then genetically programmed to use MSM as a methyl donor? It seems likely.
It is remarkable that MSM can be ingested in almost unlimited quantities by all researched life forms so far, without any signs of poisoning. In technical terms, an LD50 has never been established, which is the dosage in an experimental setup where 50% of the test animals die. On the contrary, Dr. Jacob likes to say that the test animals he examined only became fitter and more energetic as he increased the dosage.
The half-life of MSM in the body is approximately 48 hours, and after 480 hours, MSM is still detectable in the urine. This makes MSM the most stable source of sulfur and methyl groups for the body.
The discovery of MSM
Over forty years ago, Dr Robert Herschler, a chemist at the Crown Zellerbach Corporation paper mill, was asked to find a use for lignin, one of the factory’s waste products. Lignin oxidation in a reactor was found to yield DMSO (Dimethylsulfoxide), a natural, organic form of sulfur. DMSO was not a new substance, as a Russian scientist had already managed to create it in 1867 and described it in a German magazine. Initially, Crown Zellerbach focused his research mainly on the application of DMSO as a… pesticide solvent(!). One day, Dr Herschler and a co-worker got some pesticide dissolved in DMSO on their skin and subsequently became very ill. Investigations showed that the pesticide – which normally could not be absorbed through the skin – had inexplicably entered the men’s bodies. By that time, Dr Herschler had come into contact with Dr Jacob, who was particularly interested in using DMSO specifically as an antifreeze for transplant organs. They discussed the aforementioned incident and came to the conclusion that DMSO apparently had an important property that nobody yet knew about: it was able to dissolve chemicals and transfer them through the skin into the human body. Dr Jacob wondered whether DMSO could also be utilized as a transporting agent for pharmaceuticals, and commenced a series of small-scale experiments. DMSO applied to the skin was absorbed so quickly that, after just a few minutes, the subjects could taste a bitter flavour in their mouths, and their breath acquired a garlic-like odour. To his surprise, Dr Jacob discovered that DMSO itself also possessed active properties that support the skin’s regenerative abilities. Upon this discovery, Dr Jacob requested that a local highly regarded rheumatologist, Dr Rosenbaum, try DMSO in his practice. Dr Rosenbaum applied DSMO to 15 test subjects’ skins and was stunned to conclude that 13 of these patients’ conditions had improved considerably within the hour.
DMSO became a much-discussed substance. The pharmaceutical industry primarily saw it as an ideal means of transporting drugs into the body through the skin. However, in the early 1960s, the world was shocked by the ‘Thalidomide affair’. Thalidomide, a substance prescribed to pregnant women for nausea and vomiting, was found to cause congenital limb abnormalities in the fetus. In response to this affair, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) decided to suspend the approval of new drugs until further notice. As a result, the pharmaceutical industry lost interest in DMSO.
Our product range
For a healthy lifestyle
DMSO has been the subject of various international symposia. According to Dr. Jacob, over 12,000 scientific publications have been released over the years regarding the biological applications of DMSO, and 28,000 about its chemical properties. In 1970, DMSO was approved in the United States as a medication for joint problems in dogs and horses. In 1978, it was approved in the United States as a human medication for interstitial cystitis, a rare bladder condition that primarily affects women.
However, due to its bitter taste and pungent odor, DMSO never became popular among the general public. Moreover, it was found to easily cause skin irritations when applied topically. In the late 1970s, Robert Herschler initiated further research into the natural metabolites of DMSO. The research was conducted at the Oregon Health Sciences University in Portland, under the leadership of Professor Stanley Jacob. Previous research had already revealed that MSM is the main metabolite of DMSO. After being absorbed by the body, approximately 15% of DMSO is converted into MSM. Urine tests showed that orally administered DMSO was no longer detectable in the urine after 120 hours. However, MSM was still detectable after 480 hours. The delayed excretion is likely caused by MSM forming a stronger bond with body tissues than DMSO. The researchers discovered that many of the medicinal properties attributed to DMSO are likely due to its metabolite MSM. Additionally, they found that MSM is much more user-friendly than DMSO: it is more stable, odorless, and does not cause skin irritations.
For a long time, the application of MSM remained limited to the veterinary market and cosmetics. Fear of the stringent FDA regulations was the underlying reason. It was only after the FDA relaxed its rules in the 1990s that MSM became available as a dietary supplement for humans.
Our bestsellers
Discover our products
-
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
OptiMSM® Powder
250, 500, 1.000 or 5.000 gram
From: € 23,95 -
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Natural Multivitamin
60 or 180 capsules
From: € 24,95 -
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Vitamin C powder
100, 500, 1.000 or 5.000 gram
From: € 11,95
MSM: natural or synthetic?
Many people seem to struggle with the question of what exactly the source of MSM is. Is it natural or synthetic? Is it plant-based? Some producers claim that their MSM is ‘distilled from pine trees.’ We also frequently encounter the claim that MSM is of ‘natural origin’ or even ‘organic.’ Recently, we even heard from a distributor claiming that their MSM is entirely plant-based, produced from plant oils such as flaxseed oil.
MSM is a natural substance found in the human body and many foods. The richest source of MSM is breast milk, in concentrations of no more than a few milligrams per liter.
In theory, MSM could be extracted from pine trees. However, we would then have to cut down most of the pine trees on Earth to obtain a reasonable amount of MSM. Practically, this story is therefore impossible, as is the claim that MSM is of ‘natural origin’ or ‘organic.’ All MSM available on the market today does not originate from trees, plants, or oils. You cannot isolate, extract, or cultivate MSM; it requires a chemical reaction to produce it.
The American producer Cardinal Nutrition (now: Bergstrom Nutrition) was the first to use wastewater from the paper industry as a raw material for the production of MSM. Lignin was extracted from this wastewater, which was further converted into DMS (dimethylsulfide) by binding it to sulfur. It was then converted into DMSO and then into MSM.
This is what the production process looks like:
Natural ingredient (lignin) in wastewater→ CH3 (methyl groups)
CH3 (methyl groups) → chemical process → DMS
DMS → chemical process → DMSO
DMSO → chemical process → MSM
Question: how ‘natural’ can you call MSM that is produced in this way? You can’t even call it ‘half-natural’ because it is entirely synthetic, produced through a number of production steps, starting from a ‘natural substance’ in wastewater from the paper industry.
Anyone who considers the above production process understands that it is pure deception to claim that such MSM is ‘natural’ or ‘plant-based,’ or even ‘organic,’ even if lignin from wastewater from the paper industry is used as a raw material. Instead, we must accept that all MSM sold today as a dietary supplement is synthetically produced.
A major disadvantage of wastewater is that it contains many other substances that we do not want to find in our dietary supplements, including various contaminants. For this reason, Bergstrom Nutrition decided years ago to move away from wastewater and to use DMSO from the pharmaceutical industry instead. DMS and DMSO are small and relatively simple molecules that can be easily produced synthetically and are identical to what is found in Mother Nature.
All MSM offered today is synthetically produced from DMSO and hydrogen peroxide. Because all DMSO is synthetically made, the origin of DMSO is irrelevant.
It is a misconception to believe that one MSM is ‘more natural’ than another. All commercially available MSM is synthetically made from the same raw materials. However, there is a difference, but then we must look at the quality of production and the purity of the end product.
Bergstrom Nutrition’s focus on quality and purity elevates its OptiMSM® above all others. From the beginning, Bergstrom Nutrition has pioneered the distillation process to ensure purity and safety. Experts worldwide recognize that Bergstrom Nutrition uses a superior, multi-distillation method to purify the MSM. The end product is biologically identical to MSM found in nature.
The quality of MSM
MSM has traditionally been produced by Bergstrom Nutrition in the United States. This high-quality MSM is supplied by Bergstrom Nutrition under two brand names: OptiMSM® for humans and PurforMSM® for animals.
Both qualities are equally exceptional and are the most premium available on the market today. They surpass the MSM produced by factories in China and India over the past few years. Such MSM is almost always unbranded and anonymous, making it very difficult in practice to trace the producer.
OptiMSM® and PurforMSM® stand out because they are purified through quadruple distillation. This process removes any potential impurities, leaving only pure MSM. They are supplied with certificates guaranteeing the absence of molds and bacteria, and the levels of various heavy metals are negligible or almost undetectable:
Mercury (Hg): < 0.001 ppm (mg/kg)
Cadmium (Cd): < 0.005 ppm (mg/kg)
Lead (Pb): < 0.01 ppm (mg/kg)
All other producers opt for the inexpensive Crystallization Method, where MSM is dissolved in water and then dried. This is not truly a ‘purification,’ although it is often referred to as such. Not all impurities are removed but remain present. Moreover, the water used usually contains additional contaminants that end up in the MSM crystals.
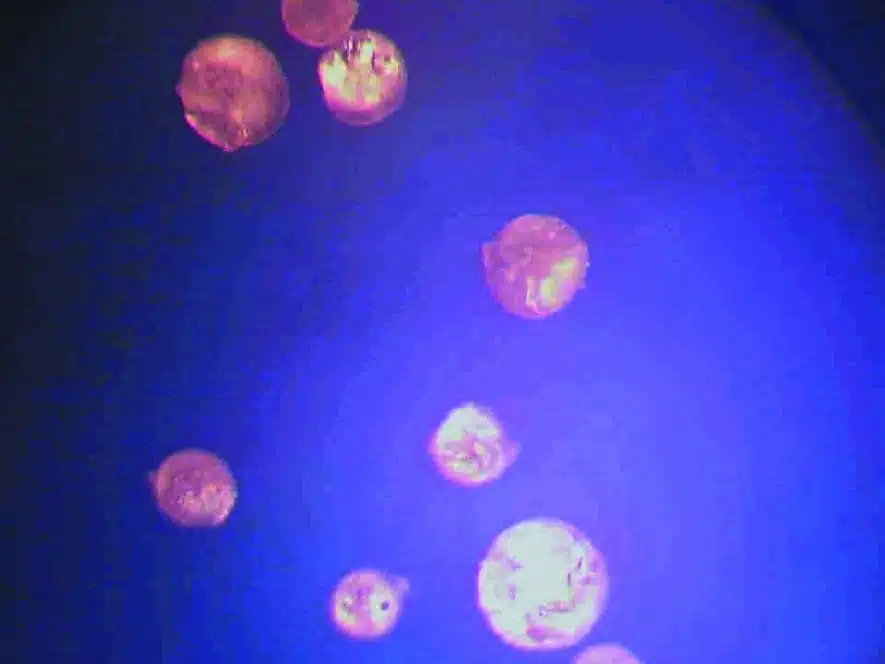
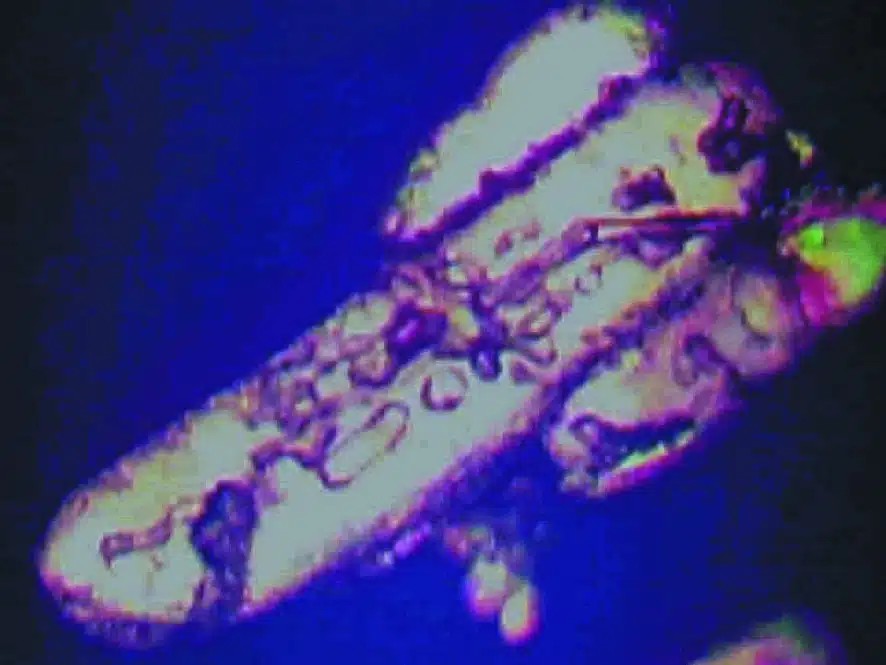
The left photo above shows a crystal of OptiMSM® after purification through quadruple distillation. There are no traces of contamination visible on the crystal. The right photo, on the other hand, shows a crystal of MSM obtained after ‘purification’ by the crystallization method. Not only does the crystal have a different shape, but there are also clearly visible traces of contamination on it. These traces could be organic contaminants or heavy metals.
Such MSM is supplied with certificates where the absence of molds, yeasts, and bacteria is often not guaranteed. Heavy metals are usually not given individually but guaranteed as a ‘group’ to < 20 ppm or < 10 ppm.
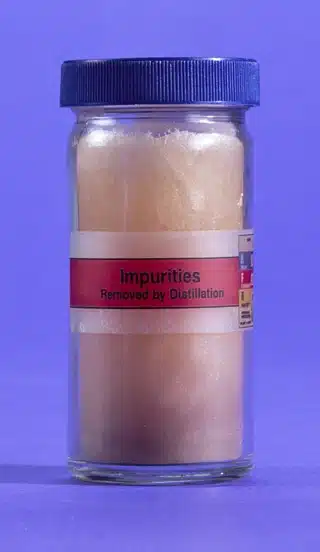

Heavy metals or no heavy metals
The right photo shows OptiMSM® after distillation. There are no contaminants present anymore. The left photo shows the contaminants that remain in the distillation setup. These are mainly the heavy metals. These heavy metals do remain present in the MSM from other producers. Bergstrom Nutrition is the only company in the world that applies the distillation method to purify MSM.
HOW DOES DISTILLATION REMOVE CONTAMINANTS?
Bergstrom Nutrition uses the expensive distillation method to purify MSM. In this method, MSM is heated to its boiling point (238ºC). The MSM vapor is collected, cooled, and crystallizes back into MSM crystals. This method leads to the highest purity:
1. All substances with a lower boiling point evaporate before MSM begins to evaporate. This removes especially the volatile, organic compounds that can be present as contaminants.
2. All substances with a higher boiling point remain behind. These are mainly the heavy metals.
Boiling Point
Lead (Pb): 1740º C
Cadmium (Cd): 765º C
Arsenic (As): 613º C
Mercury (Hg): 356º C
In short, the levels of heavy metals in OptiMSM® and PurforMSM® are guaranteed to be up to 20,000 times lower than in other MSM.”









 250, 500, 1.000 or 5.000 gram
250, 500, 1.000 or 5.000 gram
 60 or 180 capsules
60 or 180 capsules

 200ml
200ml