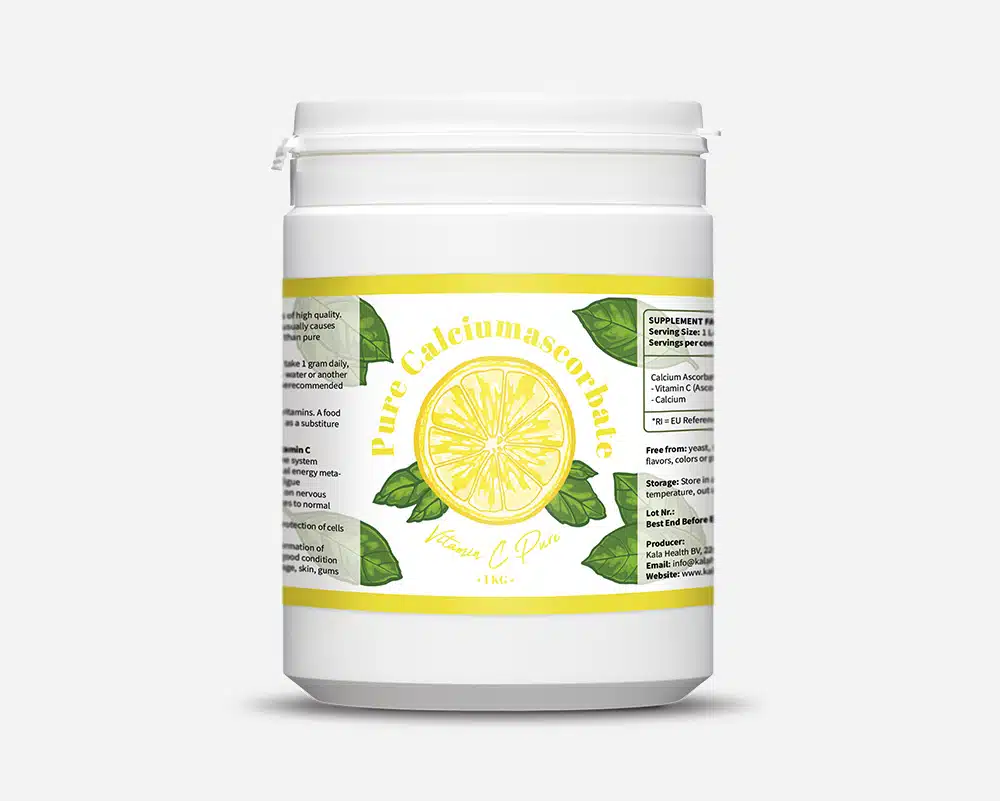
Calcium Ascorbate Powder
Calcium Ascorbate Powder
- Buffered Vitamin C: Vitamin C in the form of Calcium Ascorbate
- Gentler on the stomach: Unlike ascorbic acid, Calcium Ascorbate is gentle on the gastrointestinal system
- In a convenient powder form: Easy to dose and offers a long usage period at an affordable price
Description

What is Buffered Vitamin C (Calcium Ascorbate)?
The name ‘ascorbic acid’ is derived from vitamin C’s ability to prevent scurvy (a-scorbut = no scurvy). Vitamin C in the form of ascorbic acid has been available as a dietary supplement for more than thirty years. Approximately ten years ago, calcium ascorbate was introduced, a form of vitamin C where the ascorbic acid is bound to calcium. This dietary supplement is pH-neutral and is gentler on the stomach than ascorbic acid.
The name ‘ascorbic acid’ directly refers to the ability of vitamin C to prevent scurvy (a-scorbut = no scurvy). Vitamin C in the form of ascorbic acid has been available as a dietary supplement for more than thirty years. Due to its acidic nature, ascorbic acid causes digestive problems for many people. About ten years ago, calcium ascorbate was introduced, a form of vitamin C where the ascorbic acid is bound to calcium.
What is Vitamin C Good For?
Vitamin C has a diverse range of positive effects. According to Dutch legislation, we are limited to sharing the following effects: Vitamin C supports the formation of collagen, which is beneficial for flexible arteries and supports the maintenance of a strong vascular wall. It also supports the bones, helps release energy from food, is important for the skin, increases iron absorption, supports the immune system, supports teeth, is good for learning performance, helps with fatigue, is good for the nervous system, and is an antioxidant.
For oral advice, you can call (+31) (0)70 345-0290.
The History of Vitamin C
Scientists believe that tens of millions of years ago, a spontaneous mutation occurred in the genetic material of our distant ancestors. This mutation resulted in the loss of the ability to produce vitamin C. Since then, humans have become entirely dependent on food for their vitamin C needs. An interesting theory suggests that this evolutionary change accelerated human development. Vitamin C, an important antioxidant, was lost, which according to researchers, possibly led to a strong increase in free radicals and a large number of DNA mutations. This accelerated genetic change resulted in the emergence of various primate species, one of which eventually evolved into the ancestor of modern humans.
During ice ages and other periods of food scarcity, early humans were certainly threatened by scurvy. Probably, a new mutation ensured that early humans could better survive these harsh periods.
How Much Vitamin C Does a Person Need?
In the EU, a recommended daily amount of 80 mg is established for an adult.
It is difficult to determine the optimal amount of vitamin C needed to fully meet the body’s vitamin C needs. A fascinating discovery is that almost all animal species can produce their own vitamin C, with the exception of a few, including humans, primates, guinea pigs, rainbow trout, and coho salmon.
Health Claims Allowed by the Health Council
Vitamin C:
- supports the immune system
- promotes resistance during and after physical exertion (such as sports) and in a cold environment with a daily intake of at least 200 mg in addition to the recommended daily intake of 80 mg
- contributes to normal energy metabolism
- helps reduce fatigue
- has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous system
- contributes to normal psychological functioning
- contributes to the protection of cells against oxidative damage
- contributes to collagen formation
- supports the good condition of blood vessels, bones, cartilage, skin, gums, and teeth
- contributes to the regeneration of the reduced form of vitamin E
- promotes the absorption of iron from food and increases iron levels in the blood
Please note:
Due to legal restrictions, not all details about this dietary supplement can be provided. However, for further questions, we can be reached at (+31) (0)70 345-0290.
Composition
Buffered Vitamin C Powder contains the following ingredient:
Ingredients
| Amount per spoon(1g): | %RI* | |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | 900 mg | 1.125% |
| Calcium | 70 mg | 9% |
* RI = Reference Intake
Guaranteed free from: Preservatives, synthetic fragrances, colors, and flavors.
Use & dosage
Recommended use
| For who? | Daily dosage |
|---|---|
| Adults | 1 gram per day |
Daily Dosage: Adults 1 gram per day, or as recommended. Preferably take during a meal. Adhere to the (recommended) daily dosage. Easy to mix with water.
Mandatory Notice: A dietary supplement is not a substitute for a varied diet. A varied, balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle are important. This product is a dietary supplement (contains vitamins).
Safety: Consult a specialist before using supplements in case of pregnancy, lactation, medication use, and illness.
Storage advice
Storage: Store in a dry place at room temperature, and keep out of reach of small children.












 180 or 365 softgels
180 or 365 softgels
 60, 180 or 365 capsules
60, 180 or 365 capsules
 60 or 180 licaps®
60 or 180 licaps®
